What is Intel Tofino that every switch passionate loves?
Intel Tofino is an intelligent Fabric Processor (IFP) or a programmable switch ASIC. This next-generation ASIC offers a flexible, open, and P4 programmable data plane, NOT offered by traditional switch ASICs, which are fixed-function that provides a defined and limited set of functionalities provided by the ASIC manufacturer.
If switching, routing, or data centers interest you, you should know about the benefits of Intel Tofino.
To understand the benefits of these programmable ASICs, let’s have some background on what is a programmable data plane. These will help you appreciate the Intel Tofino switch in a better way.
Fixed Function vs. Programmable Switch
Consider the diagram below, which shows a switch ASIC.
ASIC is the most critical piece in a switch or router responsible for forwarding packets in a switch.
What you see today are mainly fixed-function ASICs.
Their data planes have fixed-function pipelines, so the switch OS can only program them for those functions; on the other hand, programmable ASICs are open and offer the Switch OS to program it flexibly.
Still not clear?
Let’s drill it down further.
What are data plane pipelines?
They present pipelines through which packets transfer in a switch.
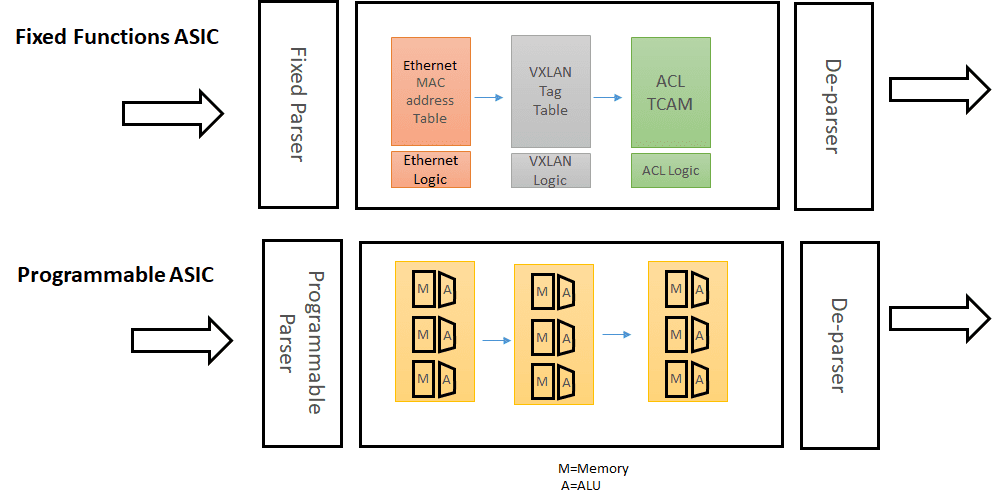
The following shows two pipelines, one for fixed-function ASIC and the other for Programmable ASIC.
This fixed-function ASIC is rigid as it supports only two types of packet processing-ethernet and VXLAN.
Here is the challenge!
What if the customer needs functions like MPLS or IP routing?
The customer, therefore, has to look for another ASIC as the current one does not support these functions.
On the other hand, the programmable ASIC has a complete programmable pipeline. The user can program each stage to be Ethernet, VXLAN, MPLS, or any other standard type (or even non-standard type).
This opens the potential for the switch to be programmed in arbitrary and often innovative ways.
What is Intel Tofino ASIC? Is it programmable?
Intel Tofino is a programmable switch ASIC using a programming language called P4.
P4 stands for “Programming protocol-independent Packet Processors”.
P4 is a language for controlling packet-forwarding planes in networking devices such as switches and routers. Instead of general-purpose languages such as C or python, it is specifically designed for networking forwarding devices.
P4 is target independent; it can program any CPUs, FPGAs, network processors, and ASICs. In general, the P4 goal is to facilitate “Protocol independent Switch Architecture,” also called PISA.
History of Intel Tofino
Tofino ASIC was developed and produced by a company called Barefoot Networks. Barefoot Networks was founded in 2013 in the US and later on acquired by Intel in 2019.
Intel saw a potential for the product and wanted to enter the ethernet switching market aggressively through programmable ASICs.
How Intel Tofino fits Intel’s Data Center evolution vision
Intel envisions the future data center to be more intelligent with diverse and large-scale workloads connected seamlessly and appear as a single computing platform. This is needed to solve the growing problem of distributed and stranded resources, and congested data flows and enable more holistic platform security.
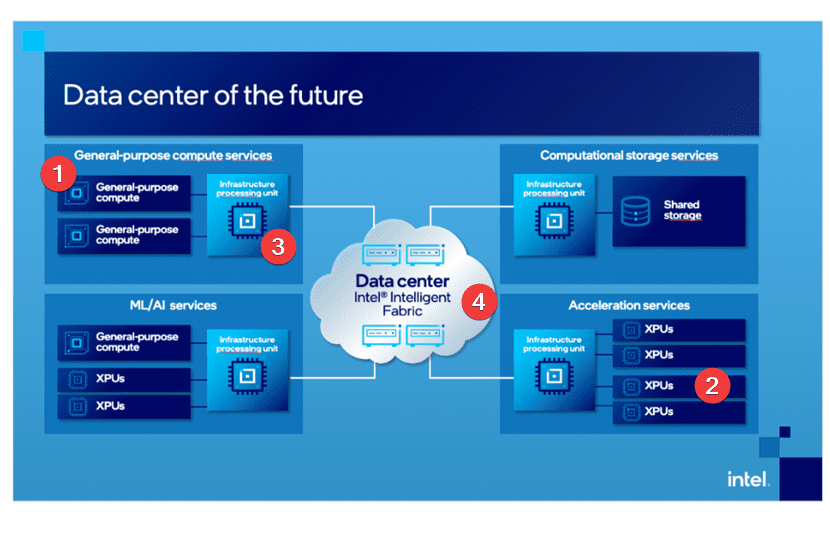
They define four necessary components, which we have marked in this picture taken from intel.com.
Three of them belong to compute, and they are
- CPU for general-purpose compute
- XPU for application-specific or workload-specific acceleration
- IPU- Infrastructure processing unit for infrastructure-specific acceleration.
Last but not least, these three components are connected through the intelligent fabric, and this is a programmable data plane using ASICs such as intel Tofino.
Different Generations of Intel Tofino (Intel Tofino 1 vs. Intel Tofino 2 vs. Intel Tofino 3)
There are different generations of Intel Tofino ASICs. Intel Tofino 1 and Intel Tofino 2 were developed by Barefoot before the acquisition, while Intel Tofino 3 is the most recent version of programmable ASIC scheduled for availability during Q2, 2022.
These different ASIC versions have different capabilities ranging throughput from 6.4 Tbps to 25.6 Tbps.
The main differences are highlighted in the following table
Intel Tofino 1 vs. Intel Tofino 2 vs. Intel Tofino 3 at a Glance ( Derived from Intel.com)
| Parameter | Intel Tofino 1 | Intel Tofino 2 | Intel Tofino 3 |
| Throughput | Up to 6.4 Tb | Up to 12.8 Tb | Up to 25.6 Tb |
| Process | 16 nm | 7 nm | 7nm |
| Num of MAU stages/pipe | 12 | 20 | 20 |
| Max SerDes speed | 25 Gbps | 56 Gbps | 112 Gbps |
| Scheduler | 1-level | 2-level | 2-level |
| Port Speed supported | Up to 100Gb | Up to 400G | Up to 400G |
| Total TCAM per pipe | 6.2 Mb | 10.3 Mb | 10.3 Mb |
Advantages/ Use cases of Intel Tofino
While there are many use cases of Intel Tofino switches like a Load balancer, network telemetry, network packet broker, Deep insight network analytics, etc we focus on two use cases here that are useful for data centers.
Use Case 1: Tofino-based Inband Telemetry INT.
In-band Telemetry (INT) is one of the first use cases for Intel Tofino switches.
INT is critical to guarantee QoS by the cloud and service provider today. It is essential to have insights into the real-time applications running inside the data centers.
Today, the cloud and service providers need to know which path the packet took, how long the packet queue at each switch, and the latency for each flow; therefore, Network Telemetry is critical.
In today’s networks, packet brokers are used to mirror the traffic. This makes the telemetry function very expensive and not easy to scale.
Thanks to P4 programmable switches such as Tofino, the telemetry function can be offloaded too
the data plane itself. This function is also called In-band telemetry (INT).
The data plane in Tofino switches can be programmed, for example, by adding metadata to each packet that reports the telemetry information as it travels through different switches.
Based on this telemetry information, insightful actions can be taken automatically using the SDN layer.
Use Case 2: Tofino-based Load Balancer
Load balancing is a critical use case in data centers. A load balancer distributes the load among different servers so that some servers are not overutilized and thus result in a consistent and better user experience.
Usually, a Load balancer in data centers is a centralized device (either a dedicated appliance or runs on a server). The incoming traffic is diverted to the load balancer first as shown below.
However, usually, load balancers are “stateful” as they need to maintain a connection state as all packets in a particular connection must be forwarded to the same server. Sometimes the connections are in millions, which means that the load balancers need to meet the performance requirements and constantly be scaled according to the traffic.
With the Intel Tofino, the load balancing function can be offloaded to the switch itself. As Tofino switch is programmable. It can offer a stateful monitoring function offering the load balancing capability with the switch itself.
Lanner’s white box with NoviMapper ( All-in-one Load balancer, packet filtering, and telemetry solution based on Intel Tofino switch)
Lanner is a leading manufacturer of white box solutions for diverse applications such as SD-WAN, Edge, Open RAN, SDN, and NFV. Lanner operates in the US through its subsidiary Whitebox Solutions ( whiteboxsolution.com).
Lanner’s white box platform HTCA ( HTCA-6600, HTCA-6400, HTCA-6200 ) is an all-in-one MEC/Edge data center open platform that includes a variety of compute blades and switchblades based on Intel Tofino ( such as HLM-1101). The platform is open to running multiple applications through Lanner’s software partners.
When combined with NoviFlow’s NoviMapper application and utilizing the power of the intel Tofino switchblade, the platform transforms into a production-ready all-in-one load balancer, packet filtering, and telemetry appliance.
Some benefits of the solution include
- A highly integrated and smart platform that requires less space and power, thus suitable for edge deployment.
- Leverages Open Standards such as OpenFlow, gRPC, and P4-Runtime
- Highly redundant platform to meet the HA needs of service provider environments
- Integrated All-in-one platform for compact needs that would otherwise require a separate load balancer, packet filtering appliance, or hardware taps.
- Open platform to support any other applications that need to run on the edge, such 5G UPF, open RAN.